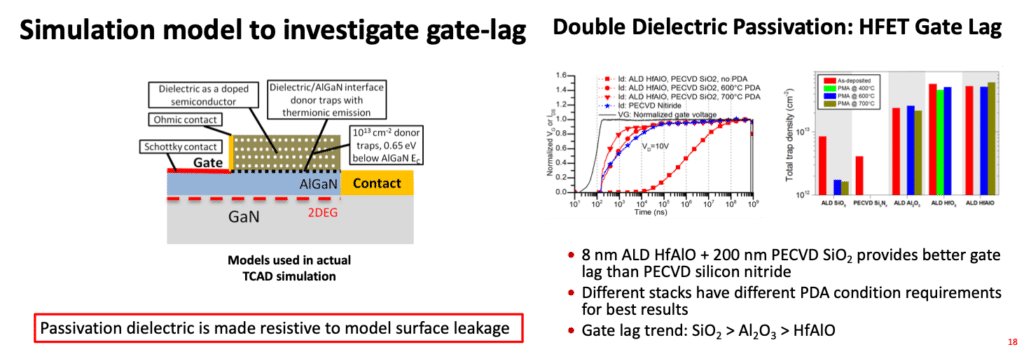
Key Contribution
Integration:
V. Misra, S. Venkatesan, C. Hobbs, B. Smith, J. Cope and E. Wilson, “Method for forming an MOS transistor having a metallic gate electrode that is formed after the formation of self-aligned source and drain regions” Patent # 5,960,270, Issue Date Sept 1999.
•Citations 279
1.This patent demonstrated a novel method to form a self-aligned reverse gate MOSFET flow (also known as gate-last). This patent is a key contribution to the field especially given that Intel has announced a gate-last process.
2.This patent has been cited by major semiconductor companies including Intel, Micron, IBM, Applied Materials, ST Microelectronics, AMD (now Global Foundries), etc.
3.Dr. Misra was the lead inventor and provided the primary integration concept of a sacrificial gate.
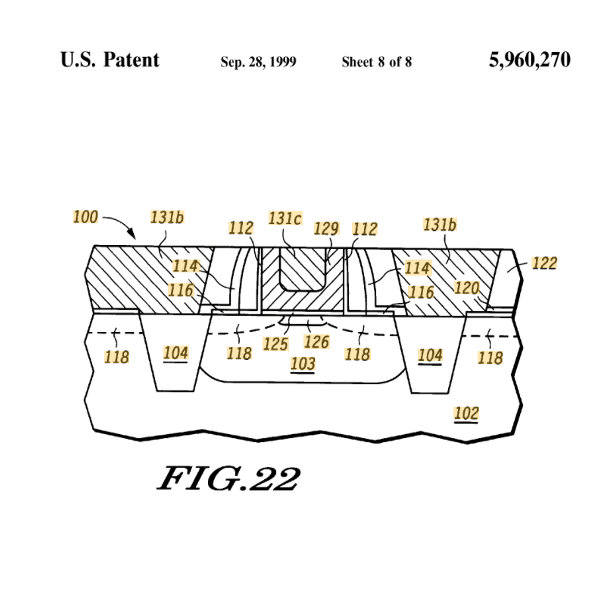
Interface Layer
RPECVD Si3N4 gatestacks with polysilicon gate electrodes were formed in situ
•Mobility values for NMOS transistors showed reduced peak values. PMOS devices showed nonexistent inversion characteristics and mobility values.
•High density of donor type states near the valence band which shifts the flatband values and reduces the involvement of hole carriers in the creating the inversion layer.
•Finally, if a 6 Å SiO2 layer was inserted between the silicon and the Si3N4 layer, full recover of the mobility was observed for both NMOS and PMOS devices.
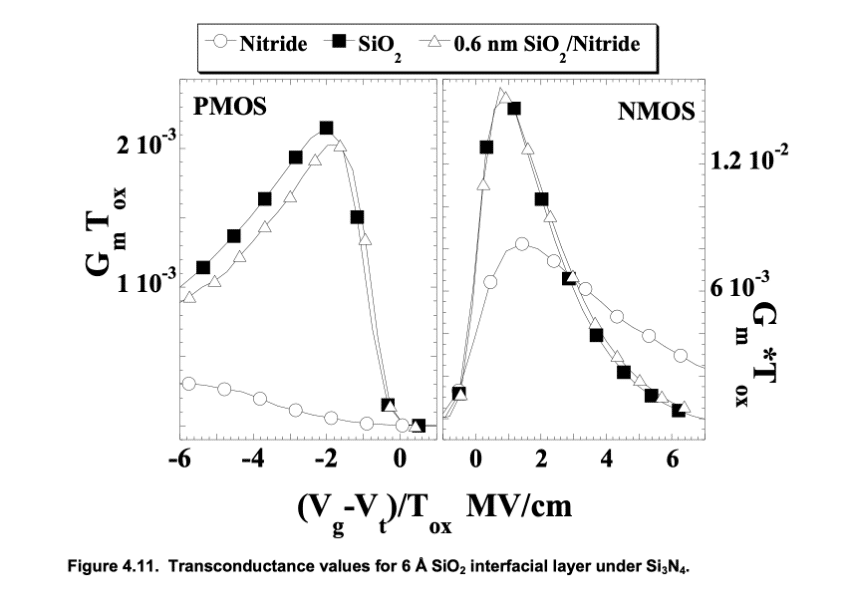
Work Function extraction
•R. Jha, J. Gurganos, Y.H. Kim, R. Choi, J. Lee and V. Misra “A Capacitance Based Methodology for Work Function Extraction of Metals on High-K Dielectrics”, June, IEEE EDL, 25(6), pp. 420-423, 2004. (Citations: 137).
•This was the first paper to present a robust approach for measuring the work function of metal electrodes by independently varying the bottom and top dielectric thicknesses. This approach extracted the effective work function which is a combination of interface reactions, dipoles or Fermi level pinning.
High K/metal Gates:
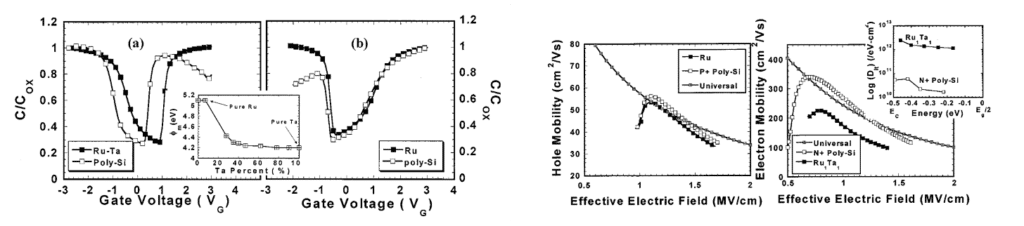
•V. Misra, H. Zhong and H. Lazar, “Electrical properties of Ru-based alloy gate electrodes for dual metal gate Si-CMOS”, IEEE Electron Device Letters, vol 23, 6, 2002. (Scopus Citations: 115). This paper was one of the first to demonstrate the feasibility of using binary metal alloys in MOSFETs by showing minimal mobility degradation under gate first MOSFET flow. Misraled this work with her graduate students Zhong and Lazar).
•
High K interfaces:
•V. Misra, G.P. Heuss, H. Zhong, “The use of MOS Capacitors to Detect Interactions of Hf and Zr gate with SiO2, APL, 78(26), pp. 4166-8, Jun. 2001. (Scopus citations: 42).
•This was one of the first papers to discuss the instability of low work function gates such as Hf and Zr and their high reactivity towards the underlying dielectric. The paper used MOS structures to understand the fundamental nature of reactivity. Misra led this work with her students: Zhong and Heuss)
•V. Misra, G. Lucovsky and G. Parsons, “Issues in high-K gate stack interfaces”, MRS Bulletin Issue, 27(3), pp. 212-216, Mar. 2002 (Scopus Citations: 41).
•This was one of the first review papers in the field of metal gatestacks that addressed the fundamental understanding of bonding and electronic structure at the high-K and metal gate interface. In this joint paper, Misra led the electrode-interface discussion).
•H. Zhong, G.P. Heuss and V. Misra, “Characterization of RuO2 Electrodes on ZrSiO4 and ZrO2 Dielectrics for Si-PMOSFETs”, APL, 78(8), pp.1134-6, Feb. 2001. (Scopus Citations: 46).
•This was one of the first papers to discuss differences between NMOS and PMOS electrodes with respect to their stability on high-K dielectrics. Both Zhong and Heuss were Misra’s graduate students who led the work).
Metal Gates:
•H. Zhong, G.P. Heuss and V. Misra, “Electrical Properties of RuO2 gates for Dual Gate CMOS,” IEEE EDL, 21(12) pp. 593-5, Dec. 2000. (Scopus Citations: 47).
•This was the first paper to evaluate the properties of a metal oxide as a gate electrode. Many groups have since continued the evaluation of metal oxides as gate candidates. Zhong and Heuss were graduate students of Prof. Misra who led the work).
•H. Zhong, H. Zhong, S.H. Hong, Y. S. Suh, G. Heuss and V. Misra, “Properties of Ru-Ta Alloys as Gate Electrodes for NMOS and PMOS Silicon Devices,” IEEE IEDM Technical Digest, pp. 467-70, 2001. (Scopus Citations: 24).
•This was one of the first papers to demonstrate that binary metal alloys can tune work function from NMOS to PMOS while also producing thermally stable films due to intermetallic bonding. This work also produced a patent.[ 6,873,020] Zhong (now at AMD), Suh (Spansion) and Heuss (Intel) were students of Dr. Misra who led the work. Hong was a post-doc.)
•B. Chen, R. Jha and V. Misra, “Work function tuning via interface dipole by ultrathin reaction layers using AlTa and AlTaN alloys”, IEEE EDL 27(9): 731-733, Sept 2006.
•(This paper proposed a novel methodology to use a dipole (Al-O-Ta) between the dielectric and metal electrode to gain large shifts in PMOS threshold voltage. This approach is advantageous since the location is removed from the bottom interface. Both Chen and Jha were graduate students of Prof. Misra who led the work.)
•J.H. Lee, H. Zhong, Y.S. Suh, G. Heuss, J. Gurganus, B. Chen and V. Misra, “Tunable Work Function Dual Metal Gate Technology for Bulk and Non-Bulk CMOS”, IEEE IEDM Technical Digest, pp. 359- 362, 2002. (SCI Citations: 38).
•This work demonstrated a novel metal gate process using ultra thin metal bilayer stacks to tune the work function values and result in ease of integration for thermally stable dual metal gates. All authors were graduate students of Dr. Misra who led the work).
•Y-S. Suh, G. Heuss, J.H. Lee and V. Misra, “Effect of Composition on the Electrical Properties of TaSiN Metal Gate Electrodes”, IEEE EDL,24 (7), pp. 439-441, 2003. (SCI Citations: 22).
•This work demonstrated that the work function critically depends on composition and a carefully controlled TaSiN layer provided both a low work function metal and excellent thermal stability. All authors were graduate students of Prof. Misra who led the work.)
•Y-S. Suh, G.P. Heuss and V. Misra, “Electrical characteristics of TaSixNy/SiO2/Si structures by Fowler-Nordheim current analysis”, APL 80 (8) pp. 1403-5, 2002. (SCI Citations: 25.
•This paper was a follow on to our initial 2001 VLSI paper, which was the first to demonstrate the use of TaSiN as a highly robust and thermally stable gate electrode. Many groups have since evaluated TaSiN in CMOS devices. Both authors were graduate students of Prof. Misra who led the work.)
Hybrid Molecular Devices (Lindsey Chem)
Gate Stacks for GaN: