Multihop Relay-Enhanced WiMAX Networks
| Sponsor: | N/A |
| Period: | July 2008 - December 2011 |
| Student: | Yongchul Kim |
Overview
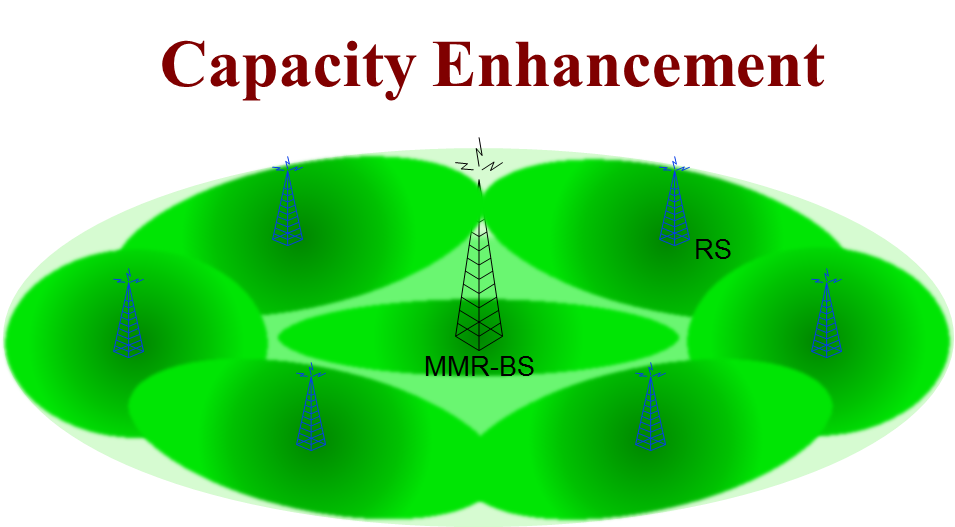
The WiMAX specification was amended (802.16j, 2009) to include multihop relays, an extension which has gained much attention and proved to be an attractive technology for the next-generation of wireless communications. New enhancements allow deployments of relay stations (RSs) that can extend the coverage of the base station (BS), increase cell capacity, or both. In this project we tackle five fundamental problems encountered in Multihop Relay-Enhanced WiMAX Networks:
- Optimal placement of RSs: A network operator always desires the minimal deployment expenditure for the provision of satisfactory service. Therefore, in order to provide efficient multi-hop relay networks, we need to know the optimal location of relay stations for maximizing network capacity.
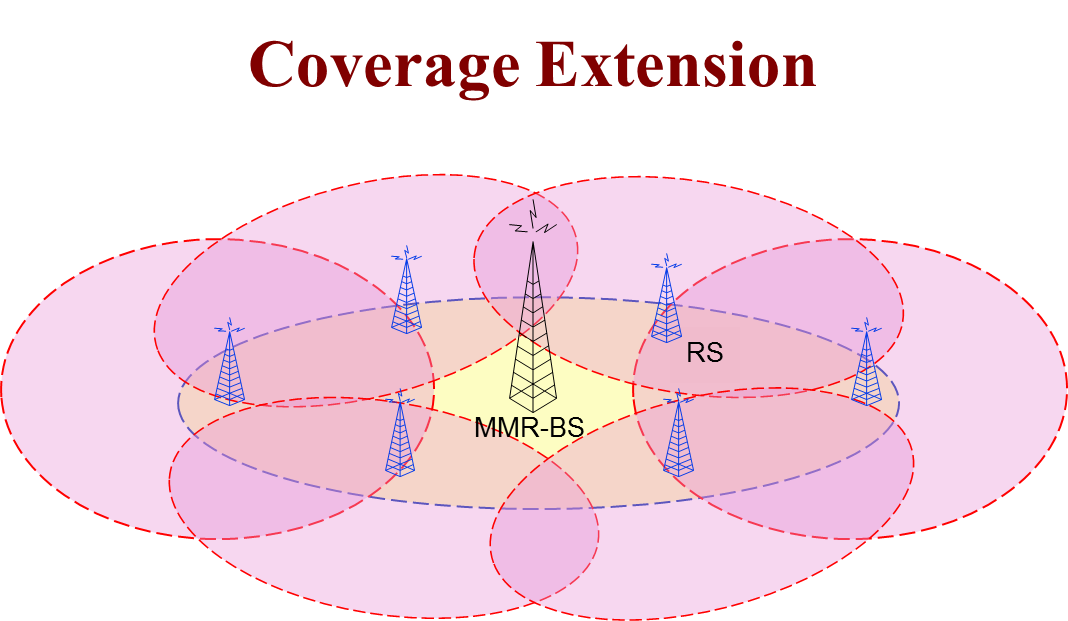
- Cost effecive coverage extension: In order to analyze the benefits of using RSs from a coverage extension perspective, we need to examine how deploying RSs affects cost and throughput as well as coverage increase.
- Fairness among active SSs: It is of interest to explore how the well known fairness schemes such as max-min and proportional fairness can be implemented in 802.16j networks. And provide another fairness scheme; subsection fairness, which can achieve more throughput than the well known fairness schemes by maximizing bandwidth utilization.
- Optimal scheduling scheme: Since it is possible that the RSs and BS are transmitting/receiving simultaneously to/from the subscriber stations (SSs) during the access zone period, it is challenging to schedule resources optimally for serving SSs in a fair manner.
- Hybrid scheduling scheme: The optimal scheduling scheme may not be applicable for a scheduler to generate a bandwidth allocation in practical WiMAX systems due to expensive operation. To attain the low time complexity scheduling scheme, we propose a hybrid resource allocation scheme that improves
the efficiency of resource utilization while minimizing interference.
Accomplishments
In this project we studied the impact of deploying RSs on both capacity and coverage aspects in relay-enhanced WiMAX networks.
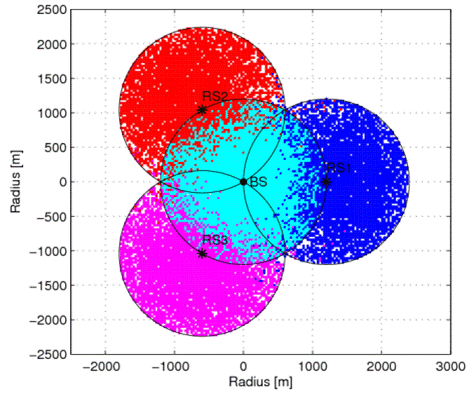
First, we presented the optimal placement of transparent RSs in WiMAX networks and showed how various network parameters such as reuse factor, terrain types, RS antenna gain, and the number of RSs can affect the optimal placement of RSs.
Second, we suggested some design guidelines allowing network operators to achieve cost-effective coverage extensions without significant throughput degradation. In general, the lower the relative cost the lower the cell throughput; however, a higher cell throughput can be achieved with lower relative cost by carefully choosing both location and number of RSs.
Third, we proposed subsection maxmin and subsection proportional schemes in order to improve the throughput in comparison with conventional fairness schemes. Our numerical results showed that the subsection max-min and subsection proportional schemes have better performance when the active SSs are non-uniformly distributed in a cell.
Fourth, we proposed an optimal scheduling scheme that maximizes cell throughput while preserving fairness among active SSs. The results showed that the cell throughput and outage rate performance can be dramatically enhanced by using the optimal scheduling scheme. We also extended our optimal scheduling scheme to a general multihop relaying scenario in order to show the impact of an increased number of relay hops on the network performance.
Finally, we proposed a hybrid resource allocation scheme that combines advantages from both the orthogonal and overlapped schemes in order to improve the efficiency of resource utilization. The results showed that the computational time of the hybrid scheme is significantly lower than the optimal scheme at the expense of the small amount of throughput degradation.
Related Publications
[1] Yongchul Kim and Mihail L. Sichitiu,
"Optimal Placement of Transparent Relay Stations in 802.16j Mobile Multihop Relay Networks" in IEICE Transactions on communications, vol. E94-B, no. 9, pp. 2582-2591, Sep 2011.
[2] Yongchul Kim and Mihail L. Sichitiu,
"Cost effective coverage extension in 802.16j mobile multihop relay networks" in Proc. of IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), pp. 1-6, 2010.
[3] Yongchul Kim and Mihail L. Sichitiu,
"Fairness schemes in 802.16j mobile multi-hop relay networks" in Proc. of IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 1-5, 2010.
[4] Yongchul Kim and Mihail L. Sichitiu,
"Optimal resource allocation in multihop relay-enhanced WiMAX networks" in Proc. of IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), pp. 1-6, 2011.
[5] Yongchul Kim and Mihail L. Sichitiu,
"Optimal max-min fair resource allocation inmultihop relay-enhanced WiMAX networks" in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 60, no. 8, pp. 3907-3918, 2011.
[6] Yongchul Kim and Mihail L. Sichitiu,
"Hybrid resource allocation scheme in two-hop relaying WiMAX networks" in Proc. of International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), 2012.
[7] Yongchul Kim and Mihail L. Sichitiu,
"Multihop Relay-Enhanced WiMAX Networks" in WiMAX/Book2, InTech, ISBN 979-953-307-675-0.


