Description of Research
Presentation of Problem
- Need For long-term, continuously operating implants
- Distributed implants
- Battery limitations
- High-bandwith communication and control
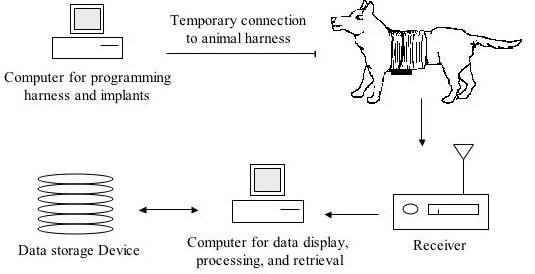
Candidate application: Cardiac Mapping
- Description of application
- Application requirements
Hypothesis
- “Magnetic Vector Steering (MVS) and Half-Cycle Amplitude Modulation (HCAM) are two techniques that enhance the state of the art in (Biotelemetry) implant technology, by providing an effective means of powering, controlling, and communicating with multiple, distributed implants. “
Research Goal
- “To use theoretical, simulation, and experimental means to prove feasibility and efficacy of MVS and HCAM with respect.
Impact of Research
- Means of providing “strategic” power delivery to distributed, arbitrarily positioned implants
- Means of Providing bidirectional, high-bandwith communications with implants
- Evaluated instance of a High-bandwith system using MVS and HCAM
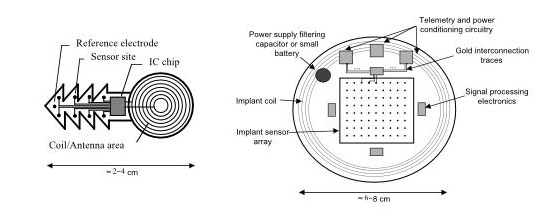
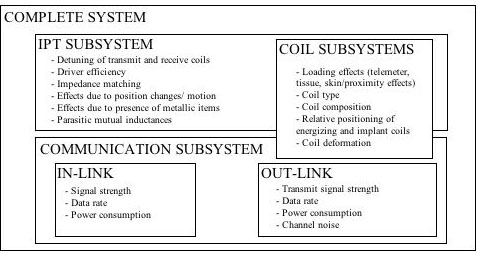
State of the Art in Electronic Implants
Three primary areas of interest:
- System architectures
- Inductive power transfer
- Communication techniques
Relevant systems
- Microstimulator technology (FNS)
- Inductive power transfer (IPT)
- In-link communication using IPT
- Out-link communication using IPT
- Distributed implant technology
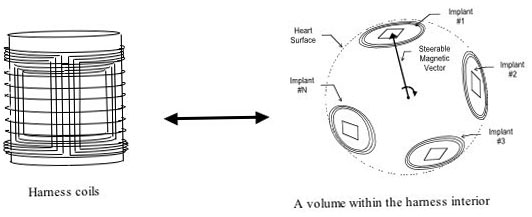
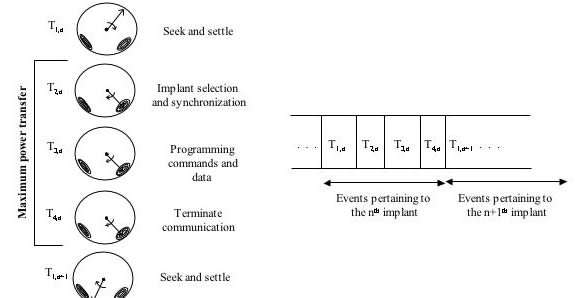
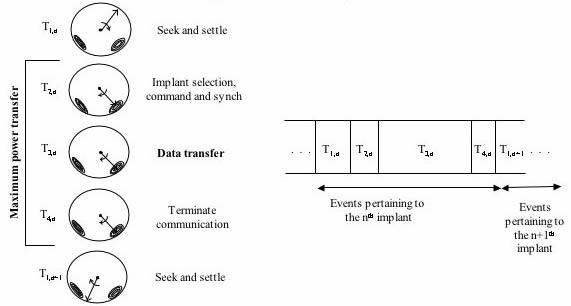
Architecture
- Focused vs. scattered power delivery
- Transmission format (in-link and out-link)
- Throughout
- Noise and interference issues
- Sensitivity
- Complexity
- Synergy
Anticipated advantages
- Low hardware overhead
- Fairly uniform magnetic field intensity
- Conserved energy
- Low sensitivity to misalignment
- Distributed energy absorption by tissue
Possible disadvantages
- Time-varying power delivery
- Delay associated with redirection of magnetic fields
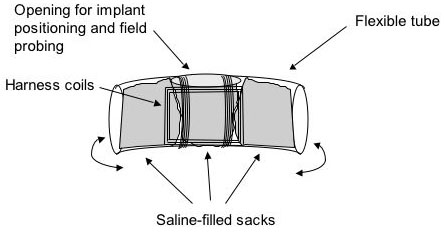
- link detuning due to repositioning/motion of harness assembly
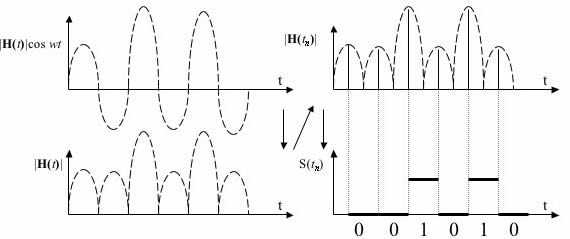
HCAM Anticipated Advantages:
- Very fast data rate
- low harmonic content
Possible Disadvantages
- Additional harmonic generation due to non-ideal switching
MVS and HCAM
Anticipated Advantages :
- Minimal interference between communications systems
- communications channel optimize for given implant during power transfer
- HCAM can be added easily to existing MVS Hardware
- Presence of power carrier can be used for subsystems
Research Activities
Goal:
- Prove feasability and efficacy of proposed techniques(MVS and HCAM)
Research Approach
- Use theorhetical investigations, simulations, and experiments to achieve goal
- Break-down proposed system into smaller units that can be analyzed effectively
- Bring together sub-units into larger units
- Optimize larger units
- Test overall system prototype
Area of focus
- Coil analysis and design
- Power electronics system and design
- Tissue loading analysis
- Implant loading analysis / implant design
- Communications systems analysis and design
- System analysis and design
- System construction
- System evaluation
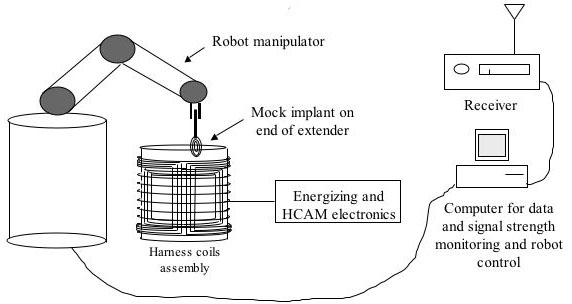
Experiments
Expected Outcomes
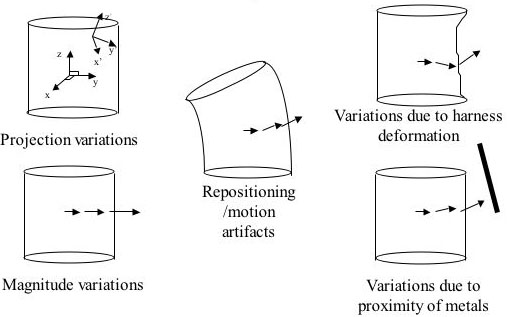
- IPT can be accomplished under a variety of non-ideal conditions
- Link loss to be significantly but not detrimentally affected by animal motion, harness deformation, and the presence of metallic objects
- Half power angle at approximately 45 degrees
- HCAM not affected by motion but possibly affected to a small degree by position
- Some degree of telemeter directionality unless there are significant reflections in the room
Accomplishments
Background investigations Simulations:
- coupling between circular loops
- modeling effects of tissue loading
Perliminary experiments:
- Power coupling between circular loops
- Experimentally determined effects of tissue loading
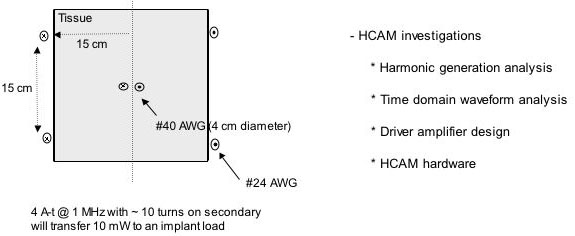
Harmonic generation analysis due to HCAM
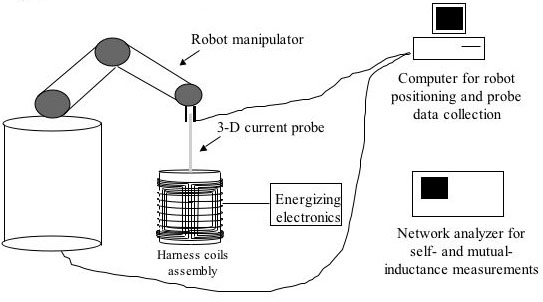
Experimental hardware:
- Energizing hardware with computer controlled amplitude and phase control
- Computer interface card
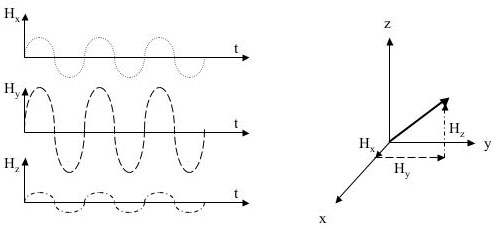
- 3-D field probe